Have you ever wondered, “What is range in math — X or Y?” You’re not alone! Many students mix up the domain and range because both are about numbers and graphs. It’s one of the most common math confusions, just like “then vs than” in English.
In this easy guide, we’ll explain what range really means, how it’s different from domain, and how to find it in equations, graphs, or real-life problems. By the end, you’ll clearly know whether range is X or Y — and you’ll remember it forever!
range meaning in math, how to find range, correct usage in graph, domain and range examples, simple math explanation, function graph tips, common math mistake, domain vs range examples
What Does Each Term Mean?
Before we decide if the range is X or Y, let’s understand both domain and range in simple terms.
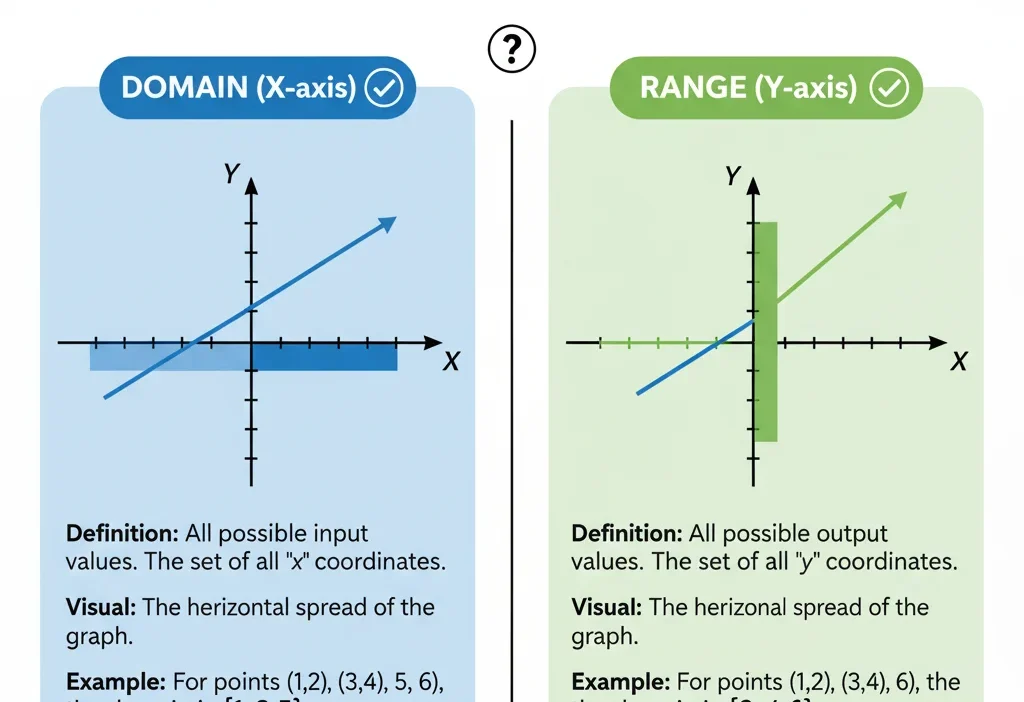
1. Domain (X values)
Definition:
The domain is all the possible input values of a function. In most cases, these are the X values.
Simple Example:
If you type a number into a calculator, that number is your input — that’s the domain.
3 Easy Examples:
- In the function y=2xy = 2xy=2x, the domain is all numbers you can plug in for xxx.
- For y=1xy = \frac{1}{x}y=x1, the domain is all numbers except 0 (since you can’t divide by zero).
- If a vending machine works for buttons 1 to 5, the domain is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
2. Range (Y values)
Definition:
The range is all the possible output values of a function. These are the Y values — what comes out after you use the domain.
3 Easy Examples:
- For y=2xy = 2xy=2x, if x=1,2,3x = 1, 2, 3x=1,2,3, then the range is 2,4,62, 4, 62,4,6.
- In y=x2y = x^2y=x2, if x=−2,−1,0,1,2x = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2x=−2,−1,0,1,2, then the range is 0,1,40, 1, 40,1,4.
- If a vending machine gives snacks A, B, or C, those are your range — the possible outputs.
The Key Difference Between Domain and Range
| Feature | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | All possible input values | All possible output values |
| Axis on Graph | X-axis (horizontal) | Y-axis (vertical) |
| Think Of It As | What you put in | What you get out |
| Example | For y=2xy = 2xy=2x: X = {1, 2, 3} | Y = {2, 4, 6} |
| Quick Tip | Domain → X → Input | Range → Y → Output |
🧠 Quick Memory Trick:
“Domain starts with D for Do (input).
Range starts with R for Result (output).”
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
❌ Mistake 1: Thinking the range is the X values.
- Wrong: “The range of y=2xy = 2xy=2x is {1, 2, 3}.”
- Right: “Those are X values! The range is {2, 4, 6}.”
Tip: Remember, range = results = Y values.
❌ Mistake 2: Mixing up axes on a graph.
- Wrong: “Domain is the Y-axis.”
- Right: “Domain = X-axis, Range = Y-axis.”
Tip: If the graph moves left to right, you’re reading the domain.
If it moves up and down, that’s the range.
When to Use Domain (X)
You use domain whenever you talk about what can go into a function.
Examples:
- The domain of y=x2y = x^2y=x2 is all real numbers.
- In y=1xy = \frac{1}{x}y=x1, xxx can’t be 0.
- For a school bus route with stops 1 to 10, those stops are the domain.
- If a machine accepts only coins, the domain is “coins.”
💡 Memory Hack:
“Domain = Data you put in.”
When to Use Range (Y)
You use range whenever you talk about what comes out of a function — the results or outputs.
Examples:
- For y=3xy = 3xy=3x, if x=1,2,3x = 1, 2, 3x=1,2,3, range = {3, 6, 9}.
- For y=x2y = x^2y=x2, range = only positive numbers.
- If your vending machine gives only chips and candy, that’s the range.
- For height vs age, the height values form the range.
💡 Memory Hack:
“Range = Result.”
Or imagine a rainbow: it ranges from red to violet — it shows all possible results.
Quick Recap: Domain vs Range
✅ Domain:
- X-values
- Inputs
- Along the horizontal (X-axis)
- Example: x=1,2,3x = 1, 2, 3x=1,2,3
✅ Range:
- Y-values
- Outputs
- Along the vertical (Y-axis)
- Example: y=2,4,6y = 2, 4, 6y=2,4,6
Super Simple Rule:
X → Domain → Input
Y → Range → Output
🌞 When to Take CoQ10: Morning or Night for Best Results? 2025
Advanced Tips (For Curious Students)
- The word range comes from “reach” — how far your function goes vertically.
- In math tests or graphs, range is always tied to Y values.
- In real life:
- Domain = all possible ingredients for a recipe.
- Range = all dishes you can make.
Pro Tip:
When you see a graph, always read left to right for domain and bottom to top for range.
Mini Quiz: Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks:
- The range of a function is all possible ___ values.
- The domain is all possible ___ values.
- In the function y=2xy = 2xy=2x, if x=3x = 3x=3, then y = ___.
- On a graph, the range is shown on the ___ axis.
- Remember: Range = ___, Domain = ___.
(Answers: Y, X, 6, Y, Result/Input)
FAQs
1. What is the range in math — X or Y?
The range in math is Y, the set of all possible output values.
2. What is the difference between domain and range?
Domain = inputs (X values), Range = outputs (Y values).
3. How do you find the range from a graph?
Look at how high and low the graph goes on the Y-axis — those Y values form the range.
4. Can domain and range be the same?
Yes, sometimes! For example, in y=xy = xy=x, both domain and range are the same numbers.
5. Why do people confuse domain and range?
Because both are about sets of numbers, but the key is: domain is what you put in, range is what you get out.
Conclusion
Now you know the answer to “What is range in math — X or Y?” The range always refers to Y values — the outputs or results of a function. The domain is the set of X values, or inputs.
Understanding this difference helps you read graphs, solve equations, and explain math more confidently. Remember: Domain → Input (X), Range → Output (Y).
Keep practicing with small examples, and soon it’ll feel as easy as reading your favorite storybook!

Oliver Thorne is a passionate digital storyteller and content strategist at WordContrast.com. With years of experience in SEO writing and online marketing, he specializes in transforming complex ideas into clear, engaging articles. Oliver loves exploring the latest trends in technology, productivity, and digital culture—helping readers stay informed and inspired in today’s fast-moving world.