Many English learners and even native speakers get confused when using expressions like p(a or b). Is it correct in writing or conversation? What does it exactly mean? People often mix it up because it looks similar to other probability or logical phrases, and the context changes its usage.
In this guide, you will learn:
- The simple meaning of p(a or b)
- How it differs from other similar expressions
- Correct usage with easy examples
- Common mistakes and how to avoid them
By the end, even beginners will be able to use p(a or b) confidently in sentences, writing, or everyday talk.
What Does Each Part Mean?
p(a or b)
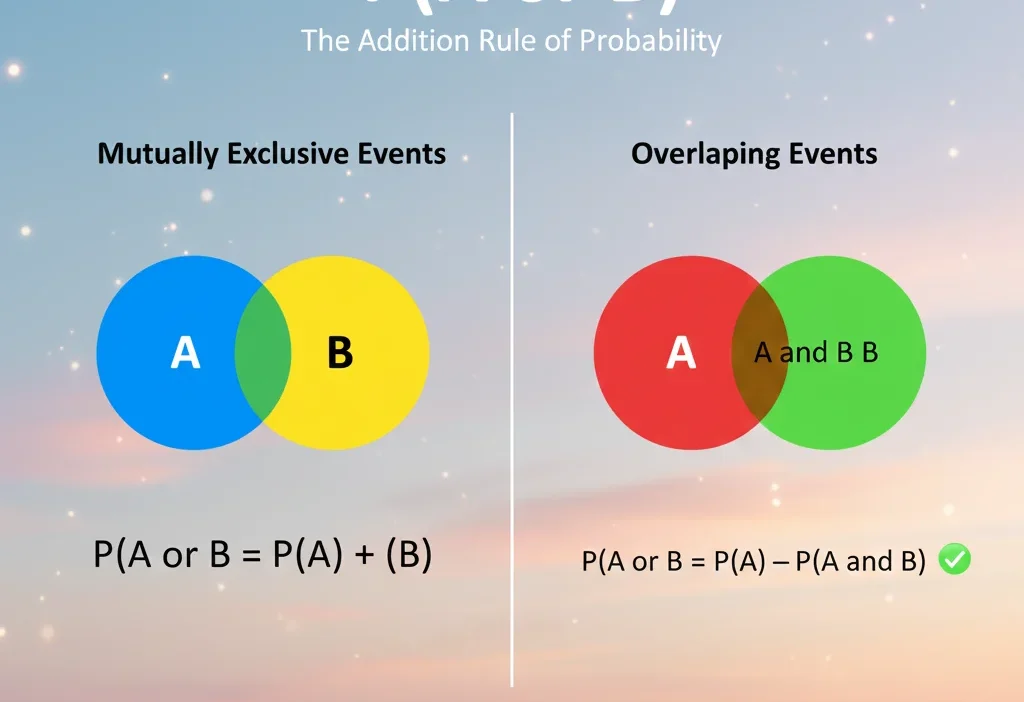
- Meaning: In probability and logic, p(a or b) refers to the likelihood that either event A or event B occurs.
- Part of Speech: It is a mathematical expression, often used in statistics or logic discussions.
Examples:
- The probability of rolling a 2 or a 4 on a die is p(2 or 4) = 2/6.
- She asked for p(rain or snow) tomorrow; the weather forecast shows a 40% chance.
- In class, we calculated p(win or draw) for our football match.
Tip: Think of “or” as giving options — either A happens, or B happens, or sometimes both.
Other Similar Expressions
Sometimes beginners confuse p(a or b) with p(a and b), which means both A and B happen together. Remember: “or” is one or the other, “and” is both together.”
The Key Difference Between p(a or b) and p(a and b)
| Expression | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| p(a or b) | Probability of A or B happening | Rolling a 2 or 4 → 2/6 |
| p(a and b) | Probability of both A and B happening | Drawing a red and a face card → 2/52 |
Quick Tip: Use “or” when you want one or the other; use “and” when you need both together.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Incorrect: p(rolling a 2 and a 4 on one die) = 2/6
Correct: p(rolling a 2 or a 4 on one die) = 2/6
Why it happens: People confuse “and” with “or.”
Incorrect: p(rain or snow) = 100%
Correct: Check actual probability — p(rain or snow) = chance of either event happening.
Why it happens: Assuming “or” always adds probabilities to 100%.
When to Use p(a or b)
Use p(a or b) in situations like:
- Probability in games – Dice, cards, or sports outcomes
- Weather forecasts – Rain or snow chances
- Daily predictions – Will it happen or not?
- Simple logic questions – Either A or B will occur
Examples:
- What is p(picking a red or blue ball) from the bag?
- Check p(pass or fail) in this exam scenario.
- The chance of meeting Tom or Jerry at the park is 50%.
- Probability of choosing pizza or burger for lunch.
Memory Hack: Imagine two boxes. One has A, the other B. p(a or b) = pick from either box.
Quick Recap: p(a or b) vs p(a and b)
- p(a or b): One or the other, or both; higher probability.
- p(a and b): Both together; lower probability.
- Use “or” for alternatives, “and” for combination.
- Remember: “Or = choice, And = combination.”
Advanced Tips (Optional)
- Origin: “Or” in English comes from Old English oþþe, meaning choice or alternative.
- Formal Writing: Use p(a or b) in statistics, reports, or exam answers.
- Online Misuse: Avoid casual misuse like “p(a or b) = 100%” in chats; probabilities are rarely that simple.
Mini Quiz
Fill in the blanks with p(a or b) or p(a and b):
- The probability of rolling a 1 ___ 6 on a die is 2/6.
- Drawing a king ___ heart from a deck is p(a and b).
- The chance of snow ___ rain tomorrow is 40%.
- Selecting a red ___ blue marble from a bag is 3/10.
- Picking a cat ___ dog from the shelter for adoption is 50%.
FAQs
- What does p(a or b) mean in simple terms?
It shows the chance that either A or B happens, or sometimes both. - How is it different from p(a and b)?
“Or” = either one or the other; “And” = both together. - Can p(a or b) be more than 1?
No, probability ranges from 0 to 1 (0%–100%). - Where can I use p(a or b)?
In games, exams, predictions, daily life decisions, or statistical problems. - Why do people confuse p(a or b) and p(a and b)?
Because “or” seems like “add everything,” but it only counts alternatives properly.
Conclusion
Understanding p(a or b) is simpler than it looks. You learned what it means, how it differs from p(a and b), and how to use it in daily life and probability problems. By practicing these examples, you will avoid common mistakes and confidently use these expressions. Remember: English and probability become fun once you see patterns, practice regularly, and enjoy learning.

Oliver Thorne is a passionate digital storyteller and content strategist at WordContrast.com. With years of experience in SEO writing and online marketing, he specializes in transforming complex ideas into clear, engaging articles. Oliver loves exploring the latest trends in technology, productivity, and digital culture—helping readers stay informed and inspired in today’s fast-moving world.