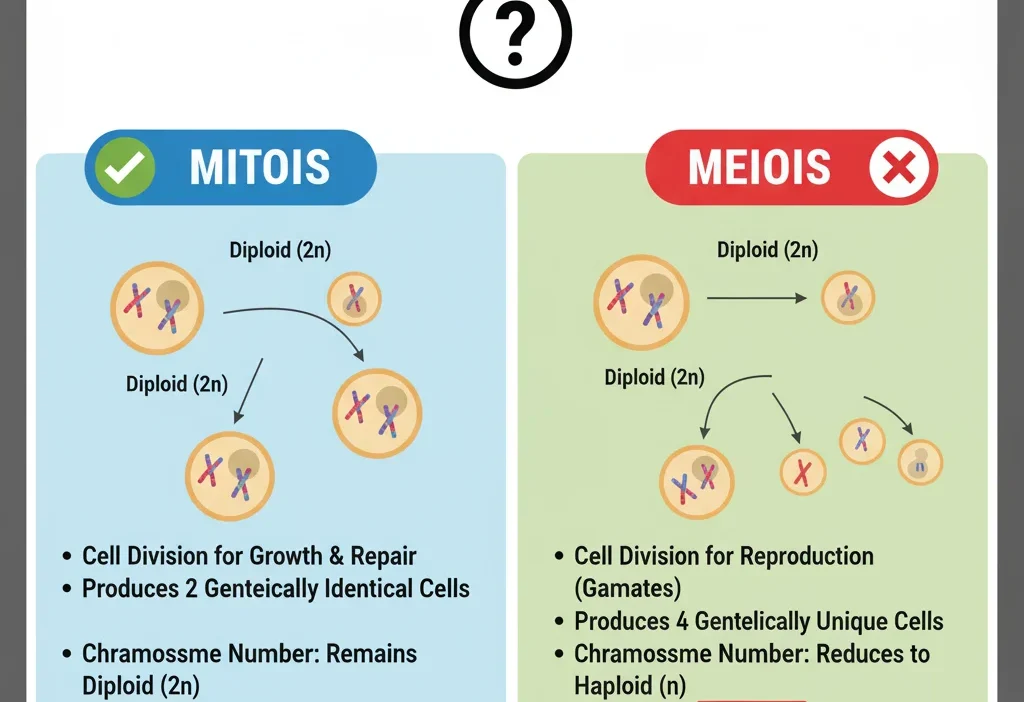
Many students ask the same question: “Is mitosis haploid or diploid?” These two biology words — haploid and diploid — sound complicated, so people mix them up. But don’t worry! This guide explains both words in a simple, clear way, using real-life examples even a 4th grader can understand.
In this article, you’ll learn what haploid means, what diploid means, and how they relate to mitosis. You’ll also see examples, a comparison table, memory tricks, and a short quiz to test yourself.
By the end, you’ll know exactly when a cell is haploid, when it is diploid, and why mitosis almost always involves diploid cells.
What Does “Haploid” Mean?
A haploid cell has one complete set of chromosomes.
Think of it like having one book of instructions.
Haploid cells are written as n.
Examples of haploid cells:
- Sperm cells
- Egg cells
- Pollen in plants
Easy Examples (Haploid)
- A sperm cell with 23 chromosomes is haploid.
- An egg cell with 23 chromosomes is haploid.
- A pollen grain that helps plants reproduce is haploid.
What Does “Diploid” Mean?
A diploid cell has two complete sets of chromosomes — one set from the mother and one from the father.
Think of it like having two copies of the same book.
Diploid cells are written as 2n.
Examples of diploid cells:
- Skin cells
- Muscle cells
- Body cells (most of your cells!)
Easy Examples (Diploid)
- A human body cell with 46 chromosomes is diploid.
- Your skin cells grow by dividing — they are diploid.
- A plant’s leaf cell is diploid.
Is Mitosis Haploid or Diploid?
Here is the simple answer:
Mitosis happens in diploid cells and creates two diploid cells.
A diploid cell (2n) divides → makes two diploid cells (2n + 2n).
But here’s something important:
✔ Both haploid and diploid cells can do mitosis.
❗ But in humans, mitosis usually begins with diploid cells.
The Key Difference Between Haploid and Diploid
Below is the simplest comparison possible:
| Feature | Haploid (n) | Diploid (2n) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of chromosome sets | 1 set | 2 sets |
| Found in | Sperm, egg, pollen | Body cells (skin, blood, muscles) |
| Can they do mitosis? | Yes, in some organisms | Yes, common in humans |
| Example in humans | 23 chromosomes | 46 chromosomes |
| Used in | Reproduction | Growth + repair |
Quick Tip to Remember
➡ Haploid = Half (one set of chromosomes).
➡ Diploid = Double (two sets of chromosomes).
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
❌ Mistake 1: “Mitosis only happens in diploid cells.”
✔ Correction: Haploid cells can divide through mitosis in many plants, fungi, and algae.
❌ Mistake 2: “Haploid cells divide to become diploid.”
✔ Correction: Haploid cells stay haploid after mitosis. They remain n.
❌ Mistake 3: “Diploid cells become haploid during mitosis.”
✔ Correction: Diploid → diploid (mitosis).
Haploid → haploid (mitosis).
Only meiosis makes haploid cells.
When to Use the Word “Haploid”
Use haploid when talking about:
✔ Reproduction
Sperm + egg = haploid cells.
✔ Cells with one set of chromosomes
Example: 23 in humans.
✔ Making new gametes (but NOT through mitosis in humans)
Simple Example Sentences
- The sperm cell is haploid.
- Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes.
- Pollen grains in plants are haploid.
- A haploid cell can divide by mitosis in many organisms.
- The egg is a haploid cell.
When to Use the Word “Diploid”
Use diploid when talking about:
✔ Body cells
Skin, muscles, hair — all diploid.
✔ Growth and repair
Mitosis in humans starts with diploid cells.
✔ Two sets of chromosomes
46 in humans.
Simple Example Sentences
- Your skin cells are diploid.
- A diploid cell divides to make two diploid cells.
- Most body cells are diploid.
- Humans grow because diploid cells keep dividing.
- Diploid cells have two full sets of chromosomes.
Memory Hack
➡ Di = two (like “di-cycle” → two wheels)
So diploid = two sets.
Quick Recap: Haploid vs Diploid
- Haploid = n = one set.
- Diploid = 2n = two sets.
- Mitosis makes exact copies of the starting cell.
- Haploid stays haploid; diploid stays diploid after mitosis.
- Human mitosis usually starts with diploid cells.
Advanced Tips (Optional)
Where the words come from
- Haploid comes from Greek haploos meaning “single.”
- Diploid comes from Greek diploos meaning “double.”
In exams
Teachers often ask:
“Is mitosis haploid or diploid?”
Correct answer:
➡ It depends on the starting cell.
➡ In humans, it begins with diploid cells.
In scientific writing
Use the symbols n and 2n when describing chromosome numbers.
In everyday language
These terms help explain growth, reproduction, and how organisms develop.
Mini Quiz: Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks:
- A sperm cell is ______ (haploid/diploid).
- Mitosis in humans usually starts with ______ cells.
- Haploid means ______ set of chromosomes.
- Diploid means ______ sets of chromosomes.
- After mitosis, a diploid cell makes ______ diploid cells.
(Answers: 1. haploid, 2. diploid, 3. one, 4. two, 5. two)
FAQs
1. Is mitosis haploid or diploid?
It depends on the start cell. Haploid stays haploid; diploid stays diploid.
2. Do humans use mitosis for haploid cells?
No. Human haploid cells (sperm and egg) do NOT divide by mitosis.
3. Which cells are diploid in humans?
Almost all body cells: skin, bones, muscles, blood.
4. Does meiosis make haploid or diploid cells?
Meiosis makes haploid cells.
5. Why do we need diploid cells?
For growth, repair, and making a complete organism.
Conclusion
Understanding whether mitosis is haploid or diploid becomes simple once you know what each word means. Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes, while diploid cells have two. Mitosis keeps the starting number the same, so haploid stays haploid and diploid stays diploid. With the examples and tips above, you can now use these words confidently in class, homework, or exams.

Celeste Rowan is a creative writer and editor at WordContrast.com, crafting compelling stories across topics like motivation, education, and personal development. She combines a warm narrative voice with data-driven insight to make her writing both relatable and reliable. Celeste believes words can spark change—and she writes to make that change happen.